Wrist Arthroscopy
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows orthopedic surgeons to visualize and treat various wrist joint conditions using a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments. This technique offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced pain, faster recovery, and improved visualization of the joint. Here’s a comprehensive and simplified breakdown of wrist arthroscopy:
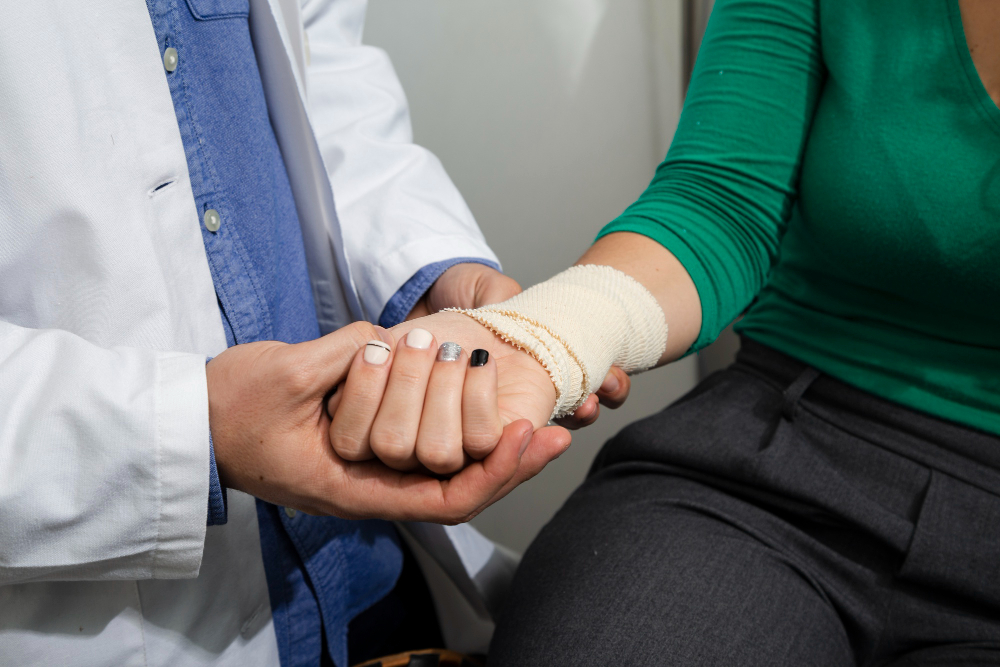
What is Wrist Arthroscopy?
Wrist arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a thin, flexible arthroscope through small incisions around the wrist joint. The arthroscope contains a camera that provides real-time images of the joint’s interior on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to diagnose and treat various wrist conditions.
Indications for Wrist Arthroscopy:
Wrist arthroscopy may be recommended for a range of wrist joint conditions, including:
- Ligament injuries, tears, or instability.
- Cartilage damage or defects.
- Ganglion cyst removal.
- Removal of loose bodies (small bone or cartilage fragments).
- Treatment of wrist fractures or dislocations.
- Evaluation of chronic wrist pain or limited range of motion.
Procedure:
The wrist arthroscopy procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: Local or regional anesthesia is administered to numb the hand and wrist.
- Incisions: Small incisions (portals) are made around the wrist to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments.
- Visualization: The arthroscope is inserted to provide clear images of the joint on a monitor.
- Treatment: Surgical instruments are used to address the specific issue, which may include repairing ligaments, removing cysts or loose bodies, smoothing cartilage surfaces, or stabilizing fractures.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips, and a bandage is applied.
Advantages of Wrist Arthroscopy:
- Smaller incisions and reduced scarring compared to open surgery.
- Minimized pain and swelling.
- Faster recovery and shorter hospital stay.
- Improved visualization of the joint’s interior.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
After wrist arthroscopy:
- Pain and discomfort are managed with prescribed medications.
- Physical therapy exercises help restore wrist strength and mobility.
- Gradual return to normal activities, with restrictions based on the surgeon’s guidance.
Risks and Complications:
While wrist arthroscopy is generally safe, potential risks include infection, bleeding, nerve or blood vessel damage, scarring, and complications related to anesthesia.
Conclusion:
Wrist arthroscopy is an advanced surgical technique that offers numerous benefits for diagnosing and treating various wrist joint conditions. It enables patients to experience less pain, quicker recovery, and improved wrist function, allowing them to regain their quality of life and return to their regular activities with enhanced comfort and mobility. Consulting with a healthcare provider and discussing the benefits, risks, and expectations of wrist arthroscopy is essential for making informed decisions about treatment.