Arthritis of the Knee
Arthritis of the knee, also known as knee osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint condition that results from the gradual breakdown of cartilage within the knee joint. This condition can lead to joint pain, stiffness, reduced mobility, and a decreased quality of life. Arthritis of the knee is common, especially among older adults, and it can be caused by various factors, including age, genetics, previous injuries, and wear and tear over time. Here’s an overview of knee arthritis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and strategies for managing the condition:
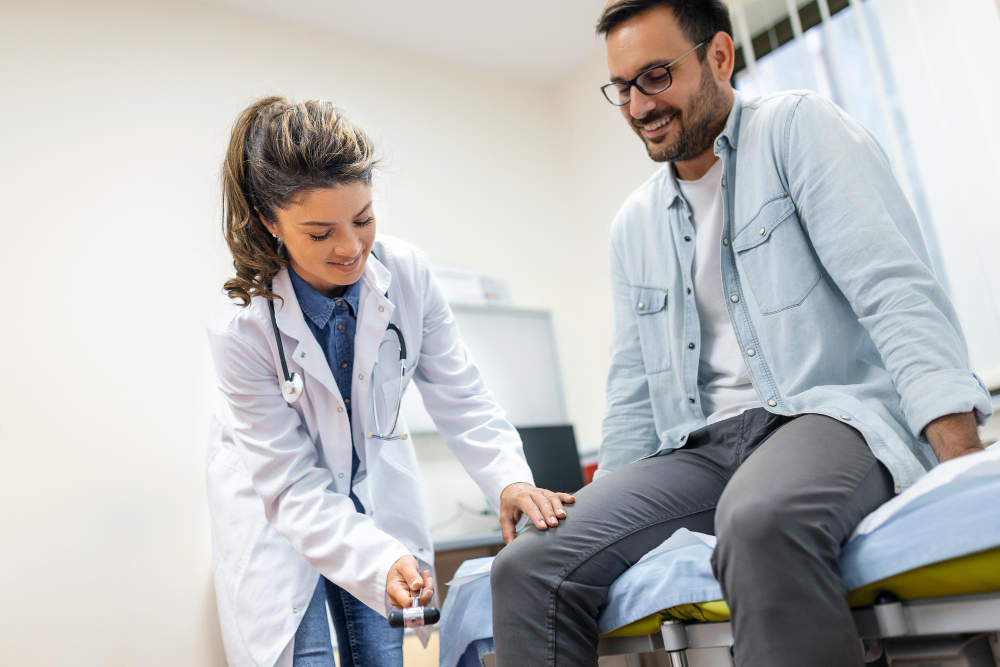

Causes of Knee Arthritis:
Several factors contribute to the development of knee arthritis:
- Age: As people age, the cartilage in the knee joint may naturally wear down.
- Genetics: Family history can play a role in predisposing individuals to arthritis.
- Previous Injuries: Previous knee injuries or trauma can increase the risk of developing arthritis.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on the knee joint, contributing to cartilage degeneration.
- Joint Misalignment: Abnormal alignment of the knee joint can lead to uneven wear on the cartilage.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of knee arthritis may include:
- Joint pain, especially during movement or weight-bearing activities.
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Swelling and tenderness around the knee.
- Joint deformity or a feeling of instability.
- Grinding or popping sensations during joint movement.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing knee arthritis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: The healthcare provider will assess the knee for tenderness, swelling, range of motion, and joint stability.
- X-rays: X-ray images can reveal joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and other signs of cartilage loss.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI may be used to assess the condition of soft tissues and cartilage within the knee joint.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for knee arthritis aims to manage symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance quality of life:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, regular exercise, and proper footwear can help reduce strain on the knee joint.
- Physical Therapy: Exercise programs can improve joint strength, flexibility, and stability.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and injections may provide pain relief.
- Assistive Devices: Canes or braces can help reduce joint stress and improve mobility.
- Surgical Interventions: In advanced cases, surgical options such as arthroscopy, realignment, or knee replacement may be considered.
Self-Care and Management:
Individuals with knee arthritis can take steps to manage their condition:
- Following a recommended exercise regimen.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint strain.
- Using assistive devices as needed.
- Practicing joint protection techniques to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Potential Outcomes:
The outcomes of knee arthritis management depend on factors such as the severity of the condition, the chosen treatment approach, and the patient’s commitment to self-care. Many individuals with knee arthritis experience improved pain relief, joint function, and overall well-being through appropriate management strategies.
Conclusion:
Knee arthritis is a chronic condition that can impact daily activities and quality of life. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and proactive self-care measures can help individuals manage symptoms and maintain joint health. If you’re experiencing knee pain, stiffness, or other symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the best strategies for managing knee arthritis and improving your overall knee health.