Knee Fracture
A knee fracture is a break or crack in one or more of the bones that make up the knee joint. Knee fractures can vary in severity, location, and type, and they may involve the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), patella (kneecap), or other smaller bones in the knee region. Knee fractures can result from various causes, including traumatic injuries, falls, sports-related accidents, and automobile accidents. Here’s an overview of knee fractures, including their types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential outcomes:
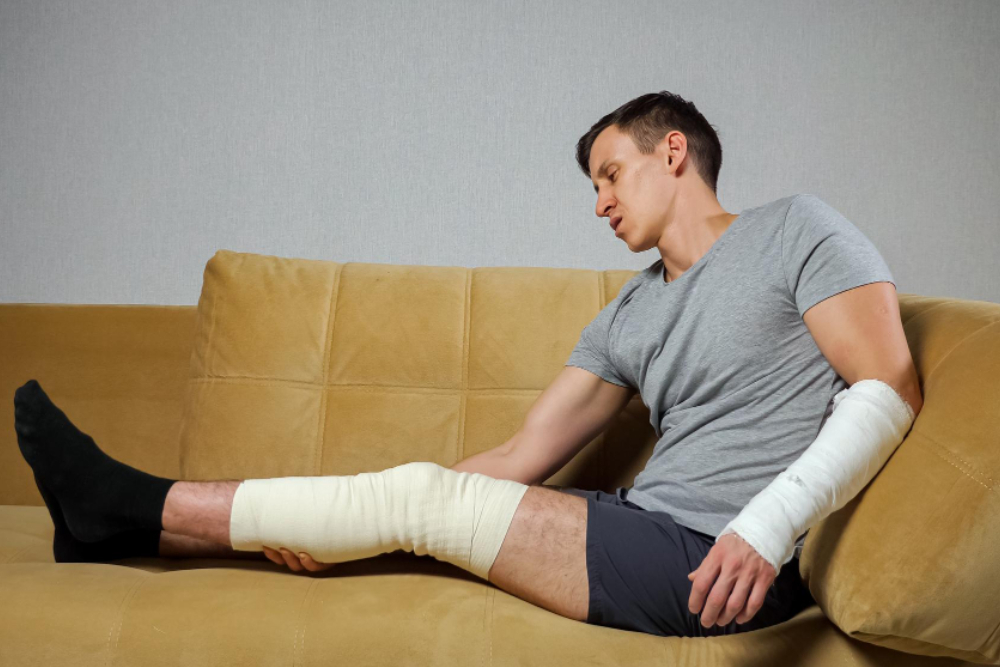

Types of Knee Fractures:
- Patellar Fracture: A fracture of the kneecap (patella) can be caused by a direct blow to the front of the knee or a fall onto a flexed knee. It may be a simple crack or a more complex fracture with displacement.
- Femoral Condyle Fracture: Fractures in the rounded ends (condyles) of the femur can result from high-energy traumas or twisting injuries. These fractures can disrupt the smooth articulation of the knee joint.
- Tibial Plateau Fracture: This fracture occurs at the top of the tibia and is often caused by a high-impact injury, such as a fall from a height. It can affect the stability of the knee joint.
- Tibial Shaft Fracture: Fractures of the tibia (shin bone) can occur in the shaft of the bone and may affect the stability of the knee.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of a knee fracture may include:
- Severe pain, swelling, and bruising at the site of the fracture.
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Deformity or misalignment of the knee.
- Limited range of motion and stiffness.
- Numbness or tingling in the affected leg (indicative of nerve involvement).
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of a knee fracture typically involves:
- Physical examination to assess the extent of injury and identify signs of fracture.
- X-rays to visualize the bones and identify the location and type of fracture.
- In some cases, advanced imaging like MRI or CT scans may be used to provide more detailed information.
Treatment:
The treatment of a knee fracture depends on the type, location, and severity of the fracture:
- Non-Displaced Fractures: These fractures may be treated with immobilization using a cast or brace to allow the bone to heal.
- Displaced Fractures: Fractures with significant displacement may require surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bones using screws, plates, or rods.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
Recovery from a knee fracture involves:
- Following the prescribed treatment plan, whether it involves surgery or conservative management.
- Using crutches or a walker to avoid putting weight on the affected leg.
- Physical therapy to regain strength, range of motion, and function of the knee joint.
- Gradual resumption of weight-bearing activities under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Potential Outcomes:
The outcomes of a knee fracture depend on factors such as the type of fracture, the treatment provided, the patient’s overall health, and adherence to rehabilitation. Many individuals experience successful healing and return to normal activities, while others may require longer recovery periods or experience lingering effects.
Conclusion:
Knee fractures can range from mild to severe and may require different approaches to treatment and management. If you suspect a knee fracture due to injury or experience symptoms such as severe pain and inability to bear weight, seeking immediate medical attention is important to ensure proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment to optimize recovery and minimize long-term complications.