De Quervains Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a painful condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It is characterized by inflammation and irritation of the tendons and their protective sheaths, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the thumb and wrist. Here’s a comprehensive and simplified breakdown of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis:

What is De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis?
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition in which the tendons (extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus) that control movement of the thumb become inflamed and irritated as they pass through the sheath at the base of the thumb.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors can contribute to the development of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis:
- Repetitive hand and wrist movements, especially those involving gripping and twisting.
- Overuse of the thumb, such as in activities like gardening, lifting, or playing musical instruments.
- Pregnancy and hormonal changes, which can affect the tendons.
- Trauma or injury to the wrist and thumb area.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis include:
- Pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist.
- Swelling and discomfort when moving the thumb or wrist.
- Difficulty grasping objects or making a fist.
- A “creaking” or “snapping” sensation when moving the thumb.
Diagnosis:
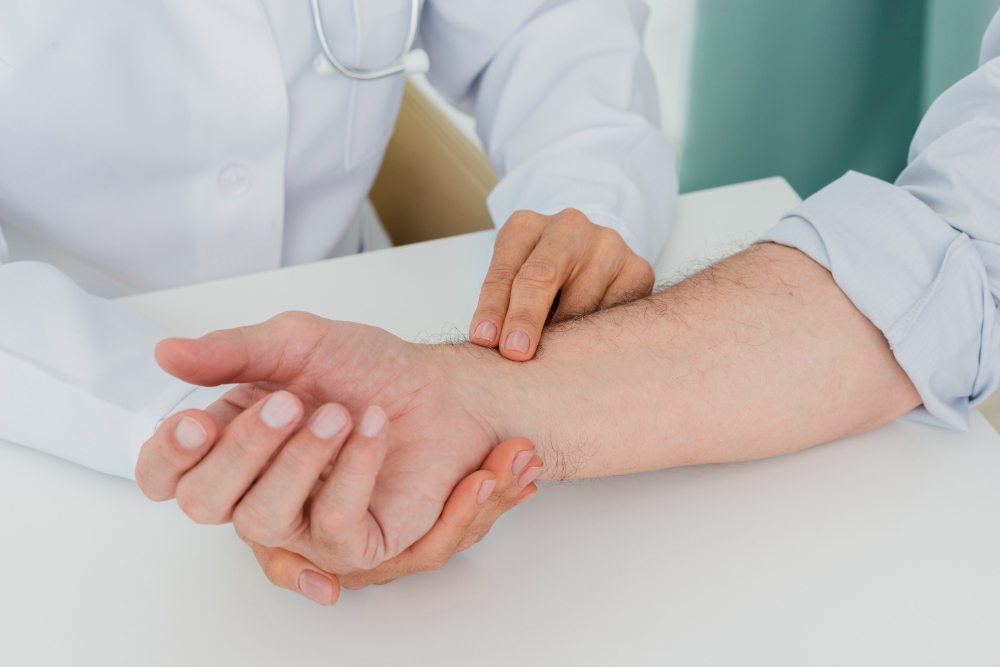
A healthcare provider diagnoses De Quervain’s tenosynovitis through:
- Physical examination to assess pain, tenderness, and thumb movement.
- Finkelstein test: A specific maneuver to reproduce the pain by moving the thumb in a certain way.
- Discussing symptoms and medical history.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis includes:
- Resting the affected hand and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms.
- Applying ice to reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and swelling.
- Wearing a splint or brace to immobilize the thumb and wrist.
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy exercises to improve thumb strength and mobility.
Prevention:
To reduce the risk of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis:
- Practice proper hand ergonomics and avoid repetitive thumb movements.
- Use ergonomic tools and techniques to minimize strain on the thumb.
- Take breaks during activities that involve repetitive thumb use.
Conclusion:
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition that can cause discomfort and limit thumb and wrist movement. Early diagnosis and appropriate management, including conservative treatments, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. Seeking medical advice when symptoms arise is essential to ensure optimal hand and wrist health.