Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, causing numbness, tingling, and pain due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. This condition is often associated with repetitive hand movements and certain medical conditions. Here’s a comprehensive and simplified breakdown of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
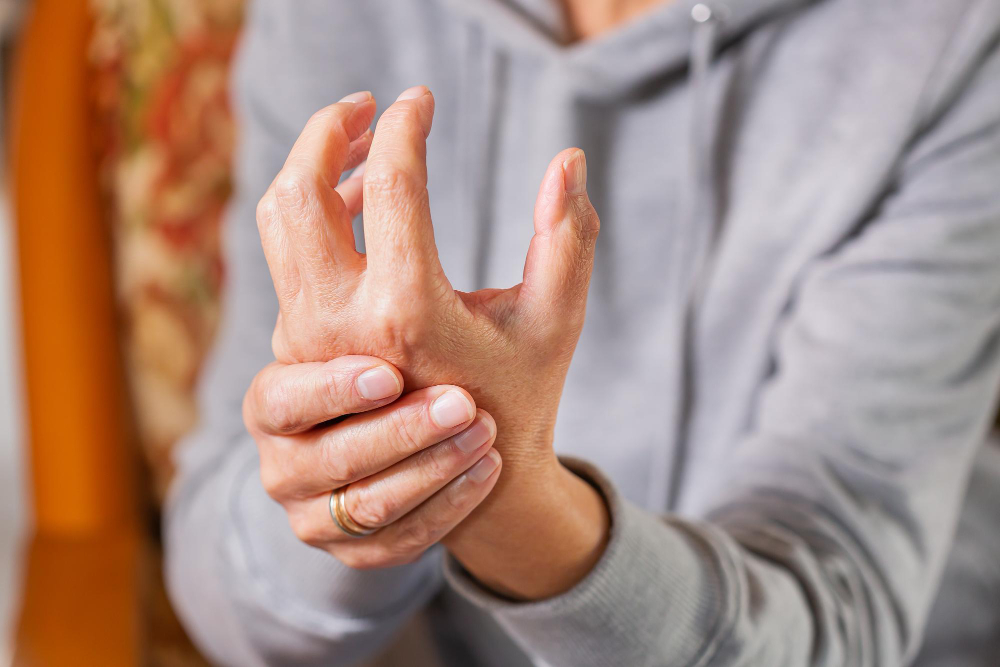

What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or irritated as it travels through the carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway in the wrist formed by bones and ligaments.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors can contribute to the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Repetitive hand and wrist movements, especially those involving typing, gripping, or using vibrating tools.
- Anatomical variations that narrow the carpal tunnel.
- Pregnancy, hormonal changes, and fluid retention.
- Medical conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disorders.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome include:
- Numbness, tingling, or burning sensation in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring fingers.
- Pain and discomfort that may radiate up the arm.
- Weakness in the hand and a tendency to drop objects.
- Symptoms often worse at night or during activities that involve flexing the wrist.
Diagnosis:
A healthcare provider diagnoses Carpal Tunnel Syndrome through:
- Physical examination to assess sensation, strength, and reflexes.
- Tinel’s sign and Phalen’s test: Specific maneuvers to reproduce symptoms.
- Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) to measure nerve function and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome includes:
- Resting the affected hand and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms.
- Wearing a wrist splint at night to keep the wrist in a neutral position.
- Applying ice to reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy exercises to improve wrist strength and flexibility.
Prevention:
To reduce the risk of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Practice proper hand and wrist ergonomics.
- Take breaks during repetitive hand movements.
- Use ergonomic tools and techniques to minimize strain on the wrist.
Conclusion:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that can cause discomfort and affect hand function. Early diagnosis and appropriate management, including conservative treatments, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. Seeking medical advice when symptoms arise is essential to ensure optimal hand and wrist health and maintain overall well-being.