ACL Reconstruction Patellar Tendon
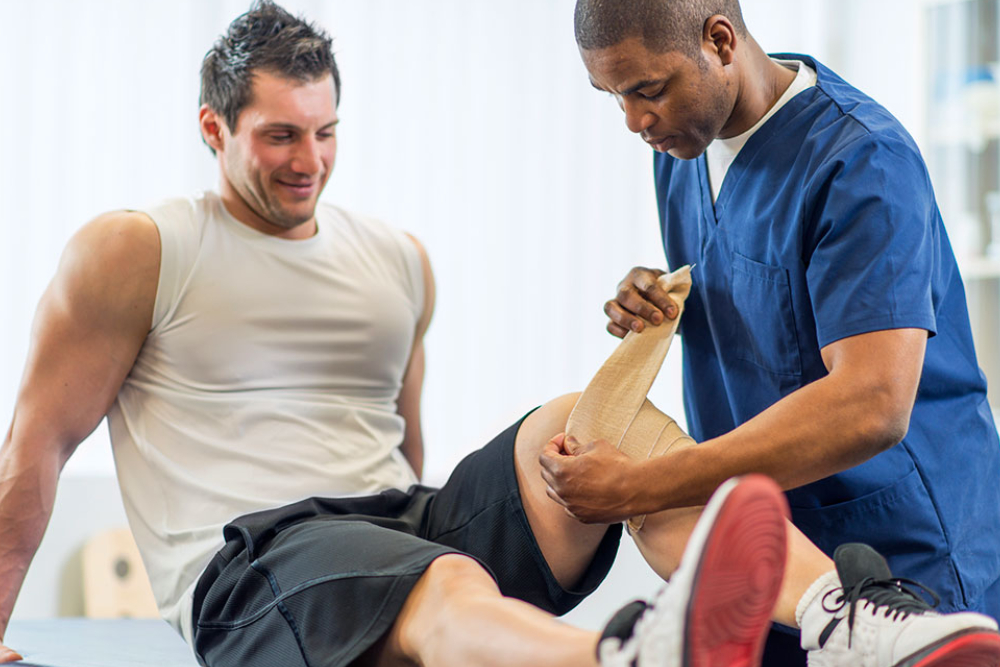
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) reconstruction with patellar tendon is a surgical procedure commonly performed to repair a torn or ruptured ACL, a key ligament in the knee. The patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia), is often used as a graft to reconstruct the torn ACL. This procedure aims to restore knee stability, improve joint function, and enable individuals to resume their normal activities, especially those involving pivoting, cutting, and jumping. Here’s a comprehensive overview of ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon graft, including its indications, procedure, recovery, and potential benefits:

Indications for ACL Reconstruction:
ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon graft is typically recommended for individuals with a complete ACL tear and those who:
- Experience knee instability and giving way.
- Participate in high-demand sports or activities that require intense knee movements.
- Have persistent symptoms despite conservative treatments, such as physical therapy.
Procedure:
ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon involves several key steps:
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered to ensure patient comfort.
- Graft Harvesting: The central third of the patellar tendon, along with bone plugs on each end, is harvested from the knee.
- Graft Preparation: The harvested patellar tendon is prepared to create a graft that resembles the original ACL.
- Tunnel Creation: Small bone tunnels are drilled in the femur and tibia to secure the graft.
- Graft Fixation: The graft is threaded through the bone tunnels and secured in place using screws, sutures, or other fixation methods.
- Joint Examination: The surgeon checks the knee joint’s stability and range of motion before closing the incisions.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
After ACL reconstruction surgery:
- Hospital stays vary based on individual factors, such as health and progress.
- A knee brace may be used initially to protect the graft.
- Physical therapy is initiated to promote healing, restore knee strength, and improve range of motion.
- Gradual resumption of weight-bearing and activities is guided by the surgeon and physical therapist.
Benefits of ACL Reconstruction with Patellar Tendon:
ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon graft offers several potential advantages:
- Strong Graft: Patellar tendon grafts are known for their strength and stability.
- Autograft: Using the patient’s own tissue reduces the risk of graft rejection.
- Good Results: Patellar tendon grafts often provide excellent stability and function for the reconstructed ACL.
Risks and Complications:
While ACL reconstruction is generally safe, it carries potential risks and complications, including infection, graft failure, blood clots, and patellar tendon issues.
Long-Term Outlook:
The success of ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon depends on factors such as the patient’s overall health, adherence to postoperative care and rehabilitation, and commitment to protecting the reconstructed knee. Many individuals successfully return to sports and activities with improved knee stability and function following successful ACL reconstruction.
Conclusion:
ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon graft is a well-established surgical technique to restore knee stability and function in individuals with a torn ACL. If you’ve experienced an ACL tear or have symptoms of knee instability, consulting with an orthopedic specialist can help determine whether ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon is a suitable option to restore knee health, alleviate instability, and enhance your ability to engage in physical activities with confidence.